Definition: Impaction of fetal anterior shoulder behind the maternal pubic symphysis. This disorder prevents progression of delivery.
Epidemiology
- Incidence varies in literature from 0.2% to 7% of cephalic vaginal deliveries (Del Portal 2014)
- No maternal or prenatal factors reliably predict shoulder dystocia
Complications
- Maternal
- Vaginal, perineal and sphincter tears
- Urinary incontinence (long term sequelae)
- Fetal
- Brachial plexus injury
- Clavicle fractures
- Hypoxic brain injury
- Death
Diagnosis
- Diagnosed clinically by inability to deliver either shoulder
- Turtle sign: fetal head may appear to retract back into the perineum
- Fetal shoulders may appear to be in a vertical axis rather than the oblique axis of a normal delivery
Initial Management
- Instruct mother to stop pushing, continued pushing could worsen impaction of anterior shoulder
- Increase the anterioposterior (AP)diameter
- Catheterize and completely drain the bladder
- Consider episiotomy
- Controversial intervention
- Retrospective review suggests a possible seven-fold risk of severe perineal trauma without reducing neonatal complications of brachial plexus injury or respiratory distress
Delivery Maneuvers
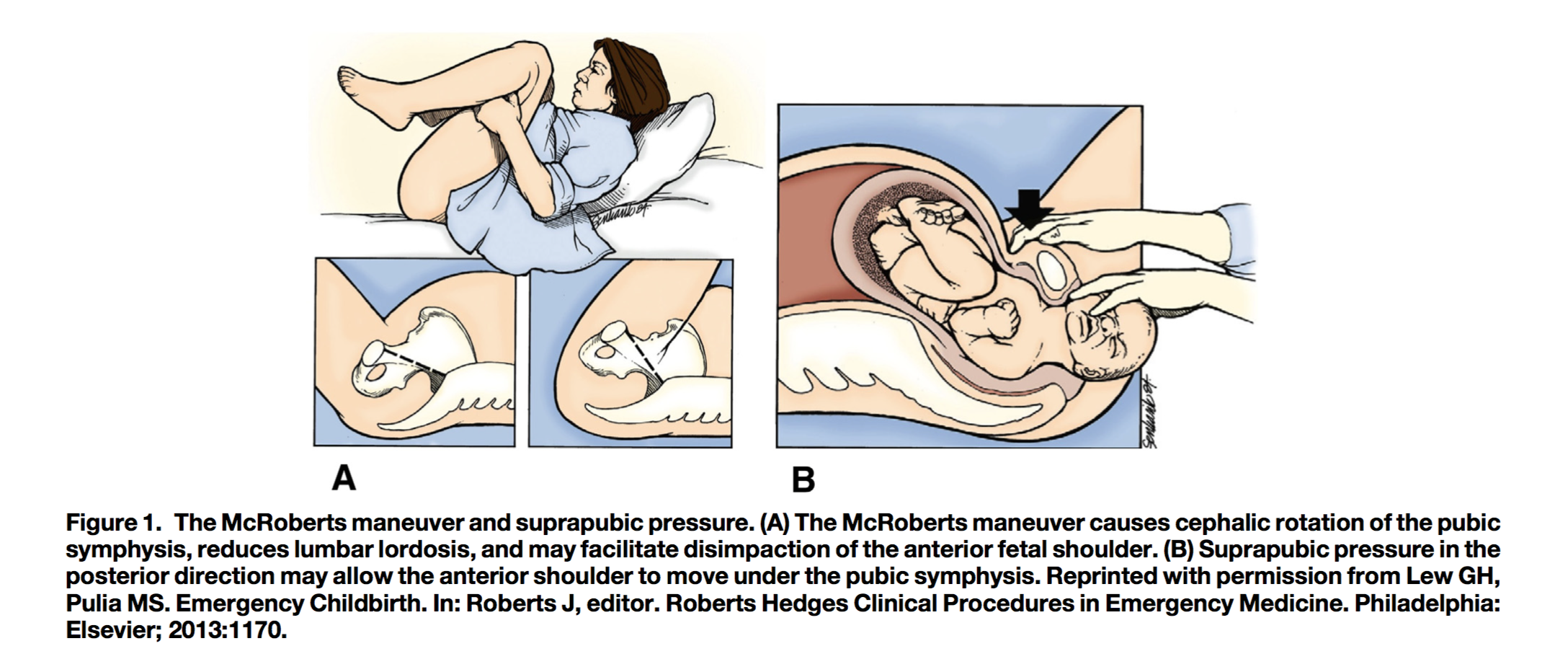
- McRoberts’ Maneuver
- Recommended first maneuver by ACOG
- Mother is lying supine with legs placed in “extreme lithotomy position” – hips hyperflexed with knees pressed to chest
- Assistants hold legs in position, one for each leg
- Causes cephalic rotation of pubic symphysis and flattening of lumbar lordosis, allows for passage of one shoulder at a time
- Resolves approximately 40% of shoulder dystocias (Del Portal 2014)
- Can be used in combination with suprapubic pressure
- Suprapubic Pressure
- Have an assistant apply suprapubic pressure while second provider applies gentle downward traction to the fetal head
- Rubin’s First Maneuver
- Suprapubic pressure applied in the lateral direction
- Helps to rotate the bisacromial diameter from anterioposterior to oblique lie
- Do not apply fundal pressure as this can worsen the shoulder impaction and risk uterine rupture
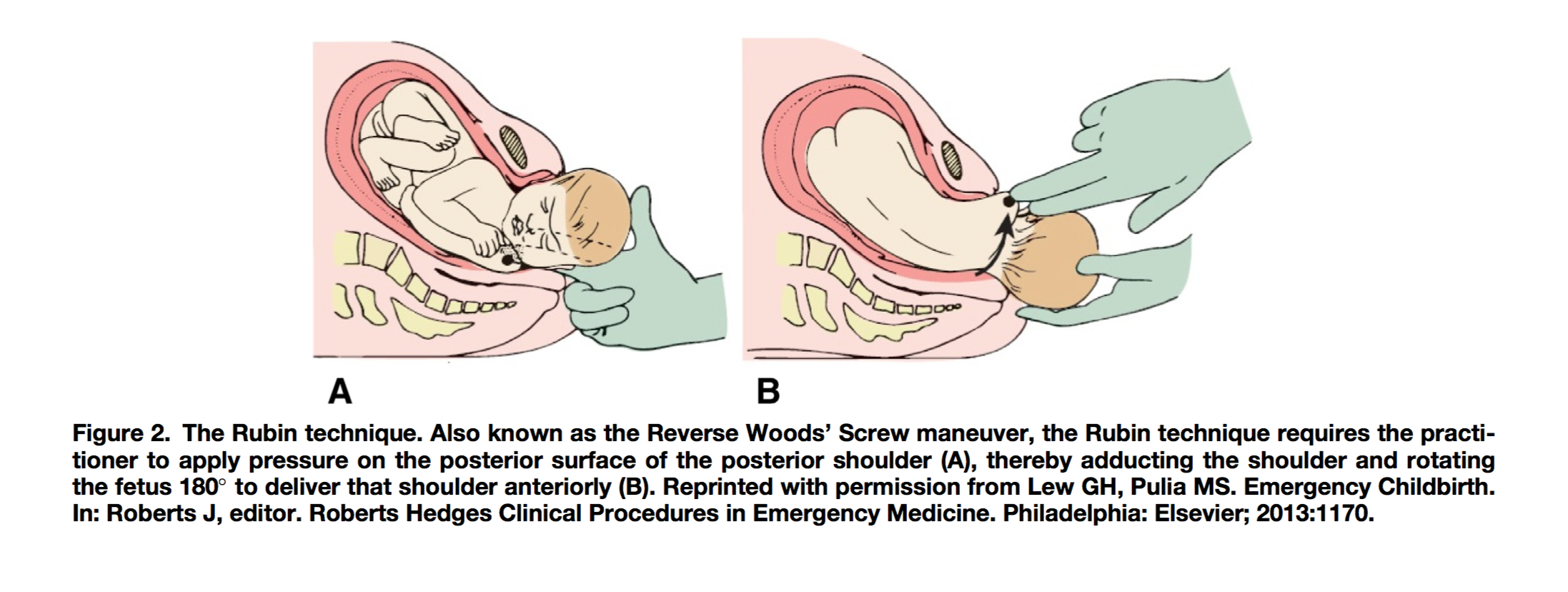
- Wood’s Screw/Reverse Wood’s Screw (Rubin Technique)
- Wood’s Screw: Insert two fingers into the vagina posteriorly and apply pressure to the anterior surface of the posterior shoulder to rotate the infant 180°
- Reverse Wood’s Screw (Rubin Technique): Insert two fingers into the vagina posteriorly and apply pressure to the posterior surface of the posterior shoulder to rotate the infant 180°
- Mazzanti Maneuver
- Suprapubic pressure applied in the posterior direction
- Pushes the anterior shoulder under the pubic symphysis
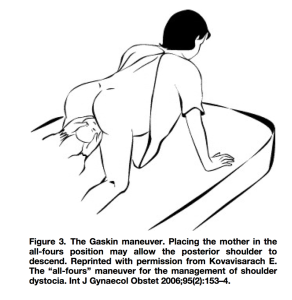
- Gaskin Maneuver
- Patient repositioned onto hands and knees and gentle downward traction is applied to the fetal head
- Allows for delivery of the posterior shoulder in more than 80% of cases(Bruner 1998)
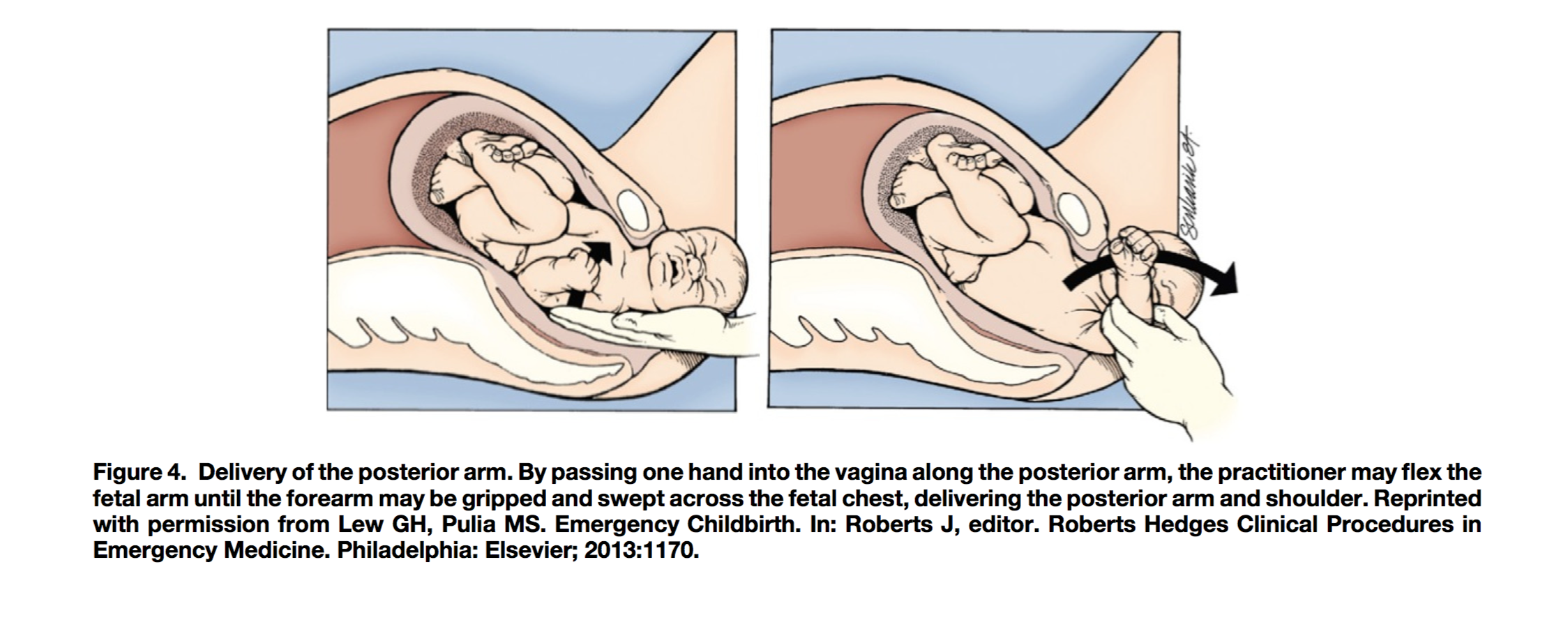
- Delivery of posterior arm
- Insert one hand into vagina along posterior arm, flex the arm until forearm or hand can be grasped and swept onto fetal chest
- Fracture of clavicle and/or humerus may result
HELPER Mnemonic
- Help: Obstetrics, neonatology, anesthesia
- Episiotomy: Generous, possibly even episioproctotomy
- Legs flexed: McRoberts’ maneuver
- Pressure: Suprapubic pressure, shoulder pressure
- Enter vagina: Rubin’s maneuver or Wood’s Maneuver
- Remove posterior arm: Splint, sweep, grasp and pull to extension
References
Bruner JP et al. All fours maneuver for reducing shoulder dystocia during labor. J Reprod Med. 1998 May;43(5):439-43. PMID: 9610468
Del Portal DA et al. Emergency department management of shoulder dystocia. J Emerg Med. 2014 Mar;46(3):378-82. PMID: 24360351
Desai S and Henderson S. Labor and Delivery and Their Complications. In: Marx, J et al, ed. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014: 2331-2350.
Gurewitsch ED et al. Episiotomy versus fetal manipulation in managing severe shoulder dystocia: a comparison of outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Sep;191(3):911-6. PMID: 15467564

Its excellent …I learnt much about shoulder dystocia and maneuvers applicable…thanks