Background
Sudden cardiac arrest has very poor outcomes; less than 11% of patients in cardiac arrest in the Emergency Department survive to discharge from the hospital. The management of cardiac arrest is algorithmic because providers have limited tools at their disposal and limited knowledge of the patient’s past medical history. EKG is limited in its evaluation of cardiac function. Pulses are often difficult to palpate. The blood pressure cuff is often unreliable. As a result, there is a sense of futility when running resuscitations.
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) in the Emergency Department gave providers another tool to help guide management through direct visualization of cardiac activity, tamponade physiology, right heart strain, etc . It also offers prognostic value if there is no cardiac activity upon arrival to the Emergency Department on TTE, there is a near 0% chance of survival. However, TTE has its limitations: obesity, emphysema, poor windows, interrupts compressions, gel gets everywhere.
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)provides significant benefits when compared to TTE in the management of cardiac arrest in the emergency department.
Clinical Question
Can transesophageal echocardiography change management in cardiac arrest in the emergency department?
Design
Case Series (6 cases)
Primary Results
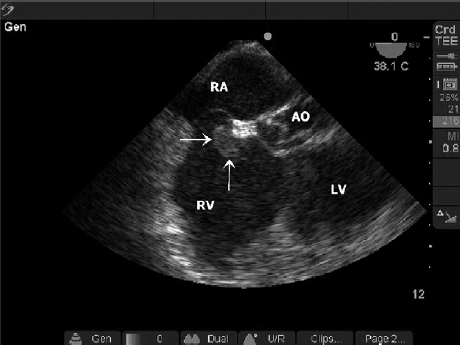
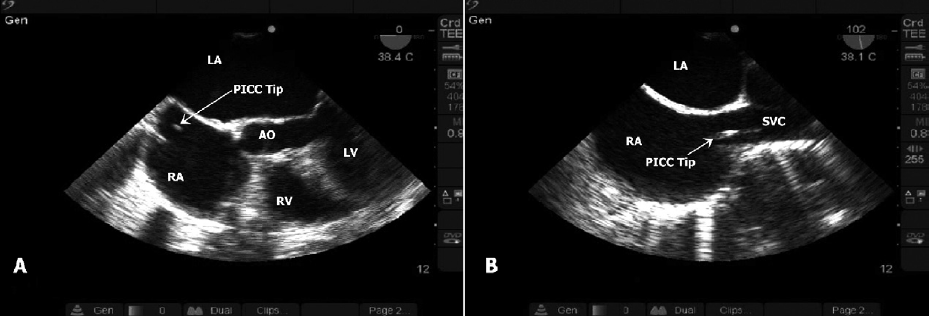
Six instances where TEE improved on bedside TTE: PICC line inserted too deep, aortic dissection, fine ventricular fibrillation, RA/RV thrombus, hyperkalemia with ventricular fibrillation, hypovolemia. In all 6 cases there was a change in management: PICC line removed, went to OR for aortic dissection surgery, shock delivered for fine ventricular fibrillation, tPA given for massive pulmonary embolism, hyperkalemia management given, volume and pressors started.
Strengths
TEE provides higher quality images than TTE, there is no need to stop compressions, the probe can be left in place without adjustment as the resuscitation goes on, the quality of compressions can be assessed in real time, subtle contractility and occult pathology is seen more easily, not affected by emphysema or body habitus, safety profile is excellent with exceedingly low rate of esophageal perforation, can cardiovert with the probe in place as it is electrically isolated.
Limitations
Expensive probe that takes time to insert, need gastric decompression, additional training is needed.
Other Issues
There was only one emergency physician performing TEEs in this series. He is a renowned ultrasonographer, but the only training described is a “commercially available 2 h instructional DVD.” It is unclear how the 6 cases were chosen, when 15 were available to chose from overall.
Author's Conclusions
“Perhaps most helpful is the ability to identify pathology with higher certainty than that allowed by most TTE scans. In summary, these cases illustrate potential advantages of TEE use in the emergency department for patients presenting in cardiopulmonary arrest. Further work will need to be performed to delineate cost effectiveness and impact on outcome as well as training requirements for focused applications.”
Our Conclusions
This case series was a proof of concept that clearly demonstrated six cases where cardiac arrest management was directly affected by TEE. This was a small cases series and it is not clear if there is a mortality benefit when applied to a larger population. However, the results are encouraging. There appear to be few drawbacks to inserting a TEE probe during cardiac arrest beyond training and the cost of the probe. The potential benefits are numerous, especially when applied to a person who is already dead.
Potential Impact To Current Practice
This article is >7 years old, however, TEE in the ED has yet to become wild-spread practice throughout emergency departments in the United States. However, there are specific programs where TEE is used regularly in the ED to help guide cardiopulmonary arrest management. No subsequent trials have been published to provide further evidence of its potential benefit.
Bottom Line
There are potential advantages to TEE use in the emergency department for patients presenting in cardiopulmonary arrest. Further research is needed to evaluate potential changes in outcomes as well as cost-effectiveness.
Read More
- Poll et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transesophageal echocardiography during cardiopulmonary resuscitation JACC 1997
- Nelson et al. The utility of cardiac sonography and capnography in predicting outcome in cardiac arrest. Int J Emerg Med. 2008
- Blaivas m . Update on point of care ultrasound in the care of the critically ill patient. World J Crit Care Med. 2012
- Brandt et al. Role of emergency intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography. J Amer Soc of Echocardiography. 1998
- Hernandez et al. C.A.U.S.E. Cardiac arrest ultra-sound exam. Resuscitation. 2007
- Neskovic et al. Emergency echocardiography. European Heart Journal. 2013
- Arntfield and Millington. Point of care cardiac ultrasound applications in the emergency department and intensive care unit – a review. Current Cardiology Review. 2012
- Usefulness of emergency ultrasound in nontraumatic cardiac arrest. Am J of Em Med. 2011
- Rebel et al. Transesophageal echocardiography for the noncardiac surgical patient. Int Surg. 2012